
What is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K was discovered in 1929 as an essential nutrient for blood coagulation (blood clotting).
The initial discovery was reported in a German scientific journal, where it was called “Koagulationsvitamin” — which is where the “K” comes from.
It was also discovered by the dentist Weston Price, who traveled the world in the early 20th century studying the relationship between diet and disease in different populations.
He found that the non-industrial diets were high in some unidentified nutrient, which seemed to provide protection against tooth decay and chronic disease.
He referred to this mystery nutrient as “activator X,” which is now believed to have been vitamin K2.
There are two main forms of vitamin K:
- Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone): Found in plant foods like leafy greens.
- Vitamin K2 (menaquinone): Found in animal foods and fermented foods.
How Do Vitamins K1 and K2 Work?
Vitamin K activates proteins that play a role in blood clotting, calcium metabolism, and heart health.
One of its most important functions is to regulate calcium deposition. In other words, it promotes the calcification of bones and prevents the calcification of blood vessels and kidneys.
Some scientists have suggested that the roles of vitamins K1 and K2 are quite different, and many feel that they should be classified as separate nutrients altogether.
This idea is supported by an animal study showing that vitamin K2 (MK-4) reduced blood vessel calcification whereas vitamin K1 did not.
Controlled studies in people also observe that vitamin K2 supplements generally improve bone and heart health, while vitamin K1 has no significant benefits.
However, more human studies are needed before the functional differences between vitamins K1 and K2 can be fully understood.
How much vitamin K should you take?
The recommended adequate intake of vitamin K you take in, both from food and other sources is below. Most people get enough vitamin K from their diets.
|
Group |
Adequate Intake |
|
Children 0-6 months |
2 micrograms/day |
|
Children 7-12 months |
2.5 micrograms/day |
|
Children 1-3 |
30 micrograms/day |
|
Children 4-8 |
55 micrograms/day |
|
Children 9-13 |
60 micrograms/day |
|
Girls 14-18 |
75 micrograms/day |
|
Women 19 and up |
90 micrograms/day |
|
Women, pregnant or breastfeeding (19-50) |
90 micrograms/day |
|
Women, pregnant or breastfeeding (under 19) |
75 micrograms/day |
|
Boys 14-18 |
75 micrograms/day |
|
Men 19 and up |
120 micrograms/day |
You should be able to get all the vitamin K you need by eating a varied and balanced diet.
Any vitamin K your body doesn’t need immediately is stored in the liver for future use, so you don’t need it in your diet every day.
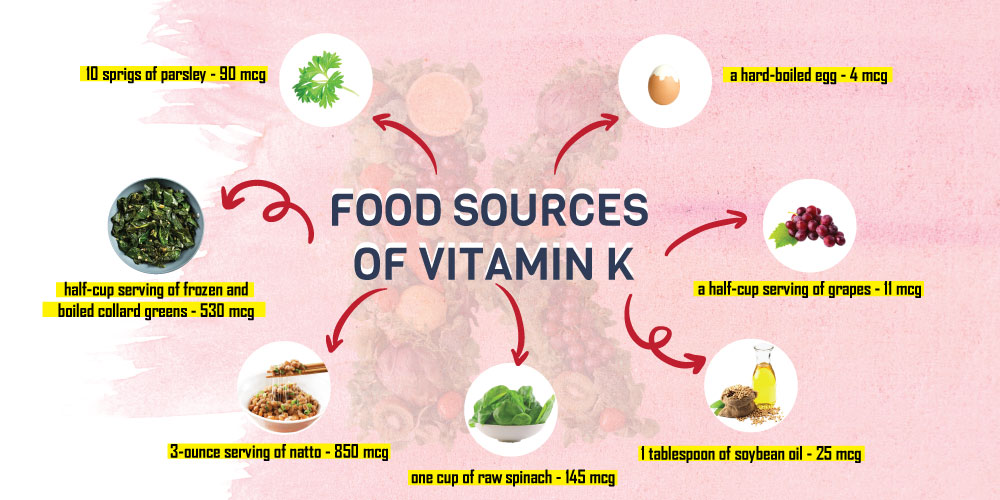
Food Sources of Vitamin K
Vitamin K1 occurs in high amounts in leafy green vegetables, such as kale and Swiss chard. Other sources include vegetable oils and some fruits.
Sources of menanoquines, or K2, include meat, dairy products, eggs, and Japanese “natto,” made from fermented soy beans.
Here are sample some food sources of vitamin K:
- 10 sprigs of parsley contains 90 micrograms (mcg)
- a 3-ounce serving of natto contains 850 mcg
- a half-cup serving of frozen and boiled collard greens contains 530 mcg
- one cup of raw spinach contains 145 mcg
- 1 tablespoon of soybean oil contains 25 mcg
- a half-cup serving of grapes contains 11 mcg
- a hard-boiled egg contains 4 mcg
What are the risks of taking vitamin K?
Side effects of oral vitamin K at recommended doses are rare.
Interactions. Many drugs can interfere with the effects of vitamin K. They include antacids, blood thinners, antibiotics, aspirin, and drugs for cancer, seizures, high cholesterol, and other conditions.
Risks. You should not use vitamin K supplements unless your health care provider tells you to. People using Coumadin for heart problems, clotting disorders, or other conditions may need to watch their diets closely to control the amount of vitamin K they take in. They should not use vitamin K supplements unless advised to do so by their health care provider.








Facebook Comments